

Git is source control system for a single developer installed on a developer desktop. Git allows you to version your changes to files. Any files can be versioned with Git, but it is typically used to version source code.
Github is a shared repository where multiple developers synchronize their changes. GitHub allows hundreds of developers all over the world work together on a single project and is the most popular open source code management platform available.
Git allows a developer to manage file versions through commits and merges. Github allows developers to commit and merge changes in centralized repository and work as teams on a single software project. So a question like Git vs Github is best answered by explaining their different roles and how Git and Github work together.
Git and Github are both based on the Git source control technology. While Git is the technology they are based on, Git also refers to the developer source control tool that is installed onto a developer workstation to manage code changes. Git is a distributed source control system. it does not prescribe a centralized repository. Historically, source control systems had a centralized architecture which made them difficult to scale.
Github and other services like it, allow development teams to create and agree on a central repository to simplify sharing changes to the master code branch. But they also keep a local copy of that repository. Every Git install comes with a repository where changes are tracked and a commit history exposes the change history. A developer working alone on a project only needs a local Git installation and repository to manage code changes. Github also tracks project changes the way a local repository does on a much larger scale.
A developer working on some code works in a project folder that has been setup as a Git repo. That developer is working on a branch. What’s a branch? A branch of code is like a draft of a written document. Say you’ve written a document and it has all of your changes and additions up to a certain point of completion, that is like a branch.
Let’s say you want to take your document draft in a certain direction, or maybe have someone else add a section to it. To do that you would create a copy and name it something like ‘document-idea-1.doc’ and make your updates, or you would send it to your friend to make updates. And if you liked those changes, maybe you’d bring those changes into your master copy. In Git, this is called merging a commit. And Git is very good at merging.
So a developer is working on a branch and wants to share the branch so another developer can make a copy of the work and continue on. Creating a copy so another developer can add changes is called branching. But how is this accomplished? You can’t really have tow people working on the same computer doing two different things.
This is where Github comes in. Github is the place where developers can share branches and accept changes from each other into the master copy (which is called the ‘master’ branch, by the way). Github allows developers to accept changes and merge them into the master branch, and then pull those changes to their local copy of the master branch and create more branches and the process continues like this. Git is the change control system for one developer and Github is where a team brings all the changes together.
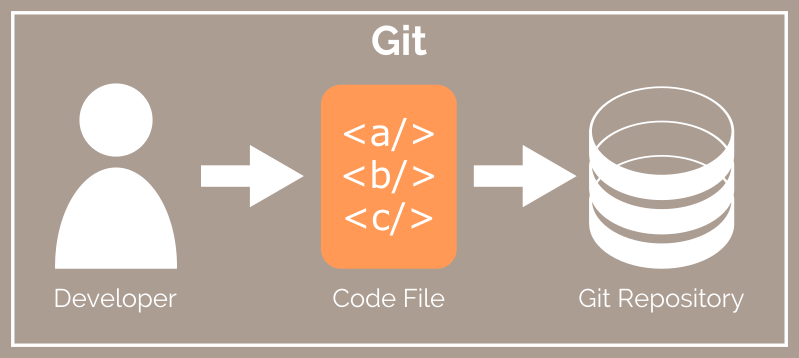
This image shows the workflow for a developer using Git. Changes made code files are detected by Git once it has been setup on a project directory with the "git init" command. These change can then be staged and committed to the local Git repository. Git always points to a "commit" in its history against which it compares changes in the developers working directory. Git has a construct called the HEAD, which is a convenience pointer to the current commit. I have a comprehensive explanation of Git HEAD in another post. While it is possible to connect two developer workstation Git repositories to share work, it gets difficult when you start adding more people to the mix.
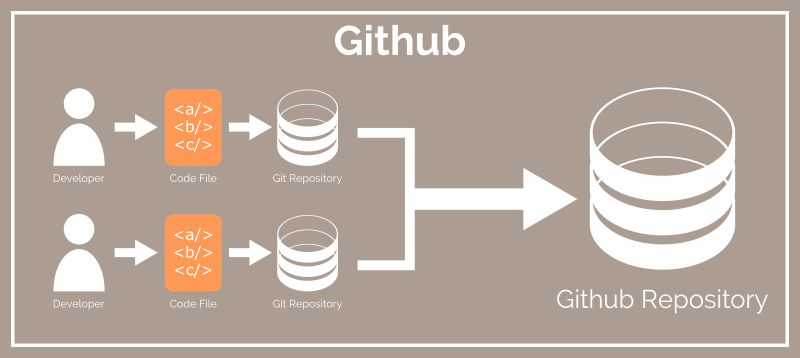
This above diagram shows a setup with two developer workstations, each running Git locally and connected to Github. Here, Github is setup as a "Git remote" where each developer's Github user account is connected to the repository. In an open source scenario, and developer can "clone" the Github repository to the their workstation and make changes to the code locally. If they choose to contribute to the code base, they can make a "pull request", which is a proposal to have their changes to the code "pulled" and merged into the master code branch.
So, if a developer only needs Git to control revisions, is there any reason why they might want to synchronize with Github? Github is essentially a Git repository sharing service, where developers can work as a team on projects, and share code, but also where a developer can share software solutions with non-developers. Github hosts many thousands of useful OpenSource projects used by hundreds of thousands of non-developers. So Github is great place for a lone developer to share out a cool solution. Github can also serve as a backup repository because it is hosted in the cloud if you lose your local Git repository, it can always be cloned from Github again and you're up and running.
Essentially, Github has the best features for OpenSource collaboration. It has bug tracking with a discussion forum, a wiki, and free hosting for open source projects. This Wired Article explains the shift to Github in detail, but it boils down to Github just being a superior platform for code sharing and collaborating.
Github desktop is a Git client UI application to help manage your local repository. Visual Studio and VSCode have Git integrations and provide convenient access to common Git operations similar to what Github desktop provides. The Git command line is always available, and this is what I use most of the time. I would lump Tortoise GIT, Git Kraken and Atlassian's SourceTree together as Github desktop competitors, and these tools could also be used to manage local Git repositories as well as remotes like Github. You definitely don't need the Github desktop to use Github. The Github website and local Git command line is sufficient.
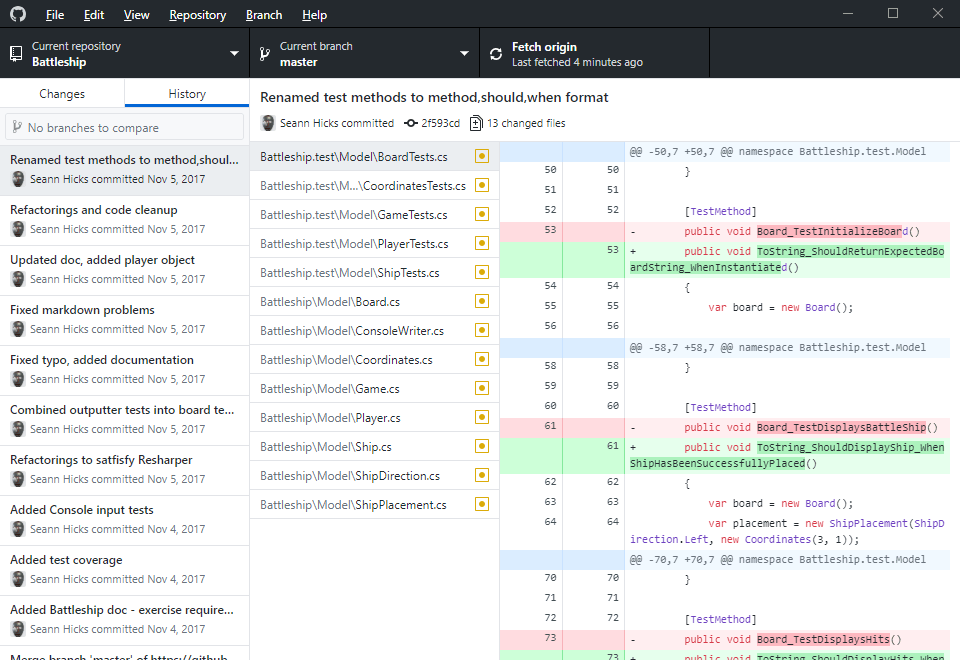
An in depth review of Github desktop is beyond the scope of this article, but here is an image of the history view of one of my Github repositories in Github Dektop. You can see all the commits I've made on the left, the files changed in the selected commit and the change "diff" (file compare) to the selected file.
So, the Git vs Github difference should be clear now. Git is the desktop tool used to manage a local project repository of code, and Github is a cloud service used by thousands of developers to share repositories with other developers and with users interested in their projects.
For more information on Git and how it works, see: